
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a non-inflammatory autoimmune disease mediated by antiphospholipid antibodies (APL). The main clinical manifestations are arterial and venous thrombosis, pathological pregnancy, and thrombocytopenia, with positive APL in medium and high titers. APL are a group of autoantibodies that target phospholipids or phospholipid-binding proteins [1-2].
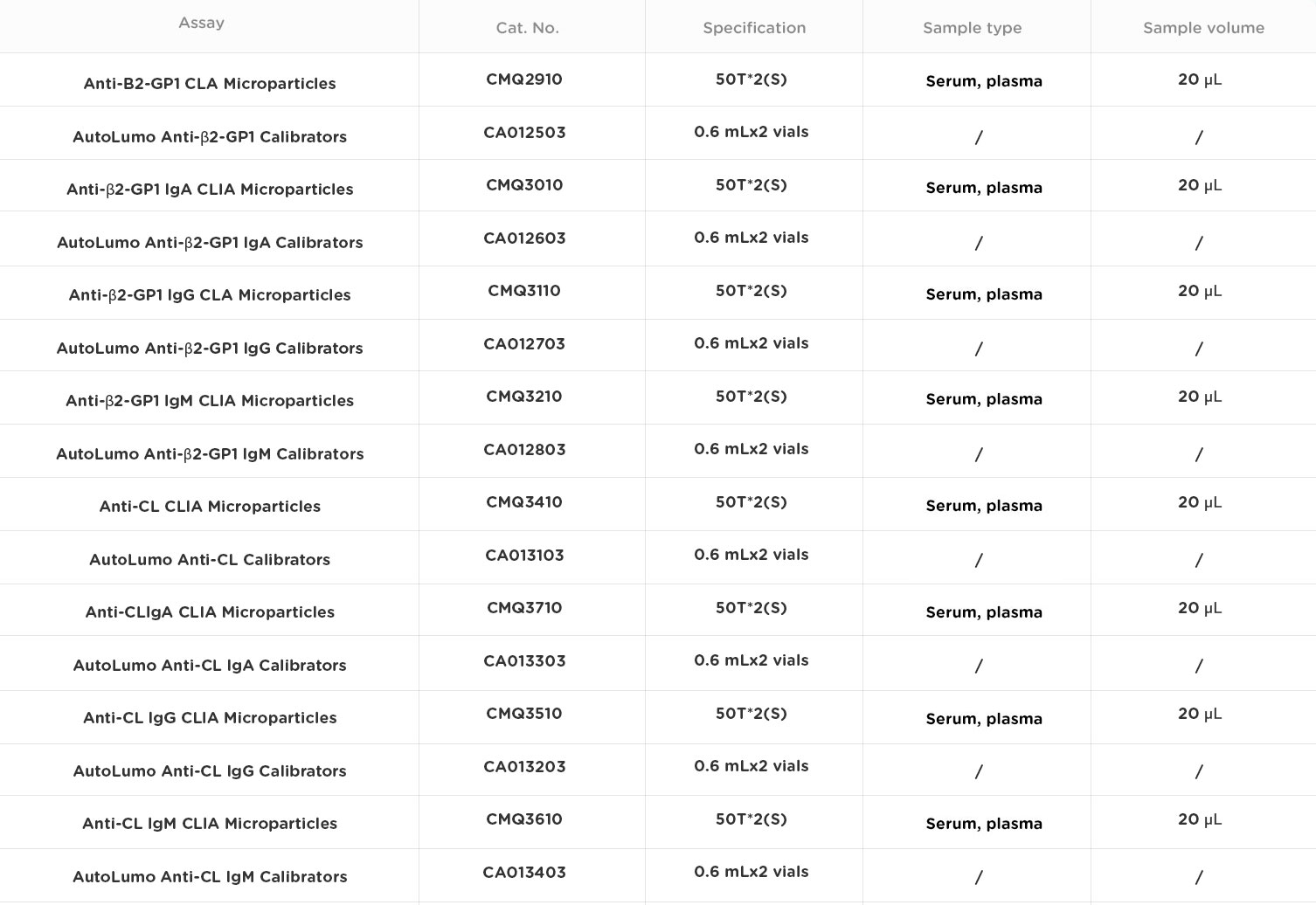
In the 13th International Consensus, the diagnosis of APS recommended the determination of IgG and IgM subtypes of anti-cardiolipin and anti-β2-GP1 antibodies, and when both are negative but APS is still suspected, the determination of IgA subtypes of anti-cardiolipin antibody is recommended. In addition, the combined detection of anti-β2-GP1 antibody and ACL is beneficial to improve the diagnostic rate of APS. The classification criteria for the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) also include the detection of antiphospholipid antibodies.
[1] Pgdg G , Bouma B , Lutters B C, et al. Structure-function studies on beta 2-glycoprotein I[J]. Journal of Autoimmunity, 2000, 15(2):87.
[2] Cetin Agar et al. β2–Glycoprotein I can exist in 2 conformations: implications for our understanding of the antiphospholipid syndrome. BLOOD. 2010,116: 1336-1343.
Address: NO.87 Jingbei Yi Rd, National Eco&Tech Zone, Zhengzhou, China
Email: info@autobio-diagnostics.com Tel: +86-371-6200-7036
Autobio Copyright Reserved for ICP 18006568. All Rights Reserved.





