Down's syndrome (DS), also called trisomy 21 syndrome, is a relatively common chromosomal abnormality disease in newborns. Its main symptoms include severe congenital intellectual disability and specific abnormal facial features. The disease has a severe impact on the child's study, life and growth. Prenatal diagnosis is an effective method to detect DS and prevent the birth of DS children. The combination of chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis and cord blood chromosome examination with clinical symptom analysis is the international golden standard of DS diagnosis.However, these assessments are to some extent invasive to the pregnant women, and requires complicated operations of healthcare professionals, and therefore are difficult for widely application. Nowadays, the most common prenatal DS screening is serum screening, which takes blood serum from the pregnant woman and measures the levels of alpha-fetal protein (AFP), unconjugated estriol (uE3), pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) and β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-HCG) to screen and detect DS.
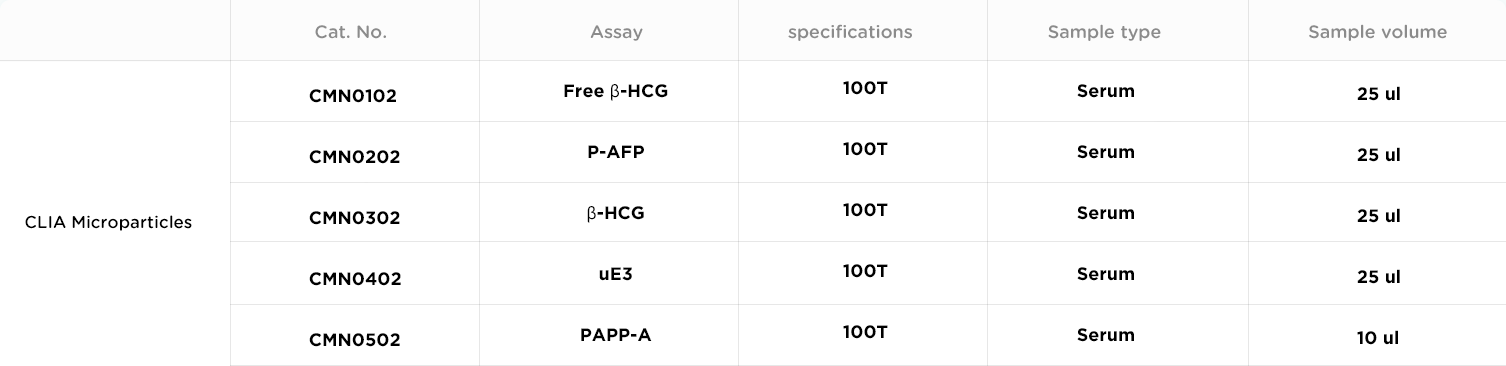
HCG is a glycoprotein hormone produced by syncytiotrophoblastic cells of the placenta. The β-HCG level in the mother's blood serum can be used to detect DS. If the fetus has DS, then the serum β-HCG level will be significantly elevated. If HCG is detected in individuals without pregnancy, it would imply tumors that can directly or ectopically secrete this hormone, for example, hydatidiform mole, invasive hydatidiform mole, choriocarcinoma, immature teratoma of ovary, dysgerminoma of ovary, glandular ovarian cancer, hypothalamic choriocarcinoma, hepatoblastoma, liver cancer, bowel cancer, pancreatic cancer, stomach cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, kidney cancer and more. Non-pregnancy HCG high-expression is primarily seen in gestational trophoblastic disease, and less commonly in other diseases.
AFP is an albumin primarily synthesized in the liver cells and vesicula umbilicalis of fetus.The AFP level in healthy pregnant women's blood will gradually increase along with fetal development, and reaches maximum during the 30th week of pregnancy.However, because DS fetuses have liver hypoplasia that leads to a reduction of AFP synthesis, the AFP level in their mother's blood would be lower than in healthy pregnant women.
uE3 is one of the three types of oestrogens produced by human. During pregnancy, uE3 is primarily synthesized by the fetal placenta, which will then enter the maternal blood circulation and be metabolized in the liver. uE3 can be used to assess the functioning of placenta and detect fetal diseases.
PAPP-A is produced by the placenta during fetal development, which prevents the maternal immune system from detecting the fetus. Its concentration in the mother's blood would rapidly increase starting from the 7th week of pregnancy. First-trimester PAPP-A level is an effective marker of DS and other aneuploidy syndromes in fetuses. In the 11th-13th weeks of pregnancy, a low PAPP-A level in maternal blood serum is often associated with stillbirth of normal chromosomal fetuses, infant death, intrauterine growth restriction, premature birth and pre-eclampsia.
[1] Juan Sheng, Analyzing the application of non-invasive genetic testing and serum screening in Down's syndrome screening [J]. Guide of China Medicine, 2019,17(12):62-63.
[2] Hoermann R, Berger P, Spoettl G, et al. Immunological Recognition and Clinical Significance of Nicked Human Chorionic Gonadotropin in Testicular Cancer. Clin Chem 1994;40(12):2306-2312.
[3] Cole LA. Immunoassay of human chorionic gonadotropin, its free subunits, and metabolites. Clin Chem 1997;43(12):2233-2243.
[4] Yingli Zhang, Therapeutic strategies of retaining the fertility function in patients with ovarian germ cell tumor [J]. Journal of Practical Obstetrics and Gynecology,2016,32(11).
[5] Patil M, Panchanadikar TM, Wagh G. Variation of papp-a level in the first trimester of pregnancy and its clinical outcome. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2014;64(2):116-119.
Address: NO.87 Jingbei Yi Rd, National Eco&Tech Zone, Zhengzhou, China
Email: info@autobio-diagnostics.com Tel: +86-371-6200-7036
Autobio Copyright Reserved for ICP 18006568. All Rights Reserved.




