


In vitro diagnostic medical devices (IVDs) are tools used to detect diseases, conditions, or infections through the examination of specimens such as blood, urine, or tissue collected from the human body. These devices perform tests outside the body, typically in laboratory settings or at the point of care. IVDs include reagents, instruments, and systems used to conduct these critical assessments, and they play a vital role in clinical decision-making and public health management.
IVDs have become indispensable in modern healthcare by enabling early and accurate diagnosis, disease prevention, and treatment monitoring. Their usage helps reduce the need for invasive procedures and facilitates personalized medicine. By providing reliable data for clinicians, IVDs support efficient healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes. Their importance was especially evident during global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, where rapid diagnostics were essential.
The IVD landscape encompasses a wide array of technologies and test formats. Common components include analyzers, reagents, control materials, and software. Key types of IVD devices include:

The global in vitro diagnostic (IVD) market is expected to grow significantly from 2025 to 2030, driven by technological innovations, an aging population, and rising demand for early disease detection. According to market research, the IVD market is projected to exceed USD 130 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5%. This upward trajectory reflects the increasing reliance on diagnostic testing in both clinical and home environments.
North America remains the dominant region in the IVD industry, supported by advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare spending. Europe follows closely due to strong regulatory frameworks and early adoption of new diagnostic technologies. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth thanks to expanding healthcare access, government initiatives, and a surge in chronic diseases. Countries such as China, India, and Japan are key players in the regional market boom.
The IVD industry is undergoing transformative changes fueled by several key trends:

Regulatory compliance is essential for bringing in vitro diagnostic devices to market. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) categorizes IVDs based on risk and requires premarket notification or approval depending on the classification. In the European Union, IVDs are regulated under the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR), which became fully applicable in 2022. Devices must bear the CE mark, demonstrating conformity with health, safety, and performance standards. Both regulatory systems prioritize safety, effectiveness, and accurate labeling.
Manufacturers must also adhere to international standards, such as:
Compliance with these standards helps manufacturers maintain product quality, ensure traceability, and pass audits by regulatory bodies.
IVD manufacturers face various regulatory challenges, including evolving laws, complex documentation, and cross-border compliance. To overcome these hurdles, companies invest in regulatory intelligence systems, hire specialized compliance teams, and maintain clear communication with notified bodies and agencies. Digital tools that track changes in international regulations also assist in minimizing delays and avoiding costly recalls.
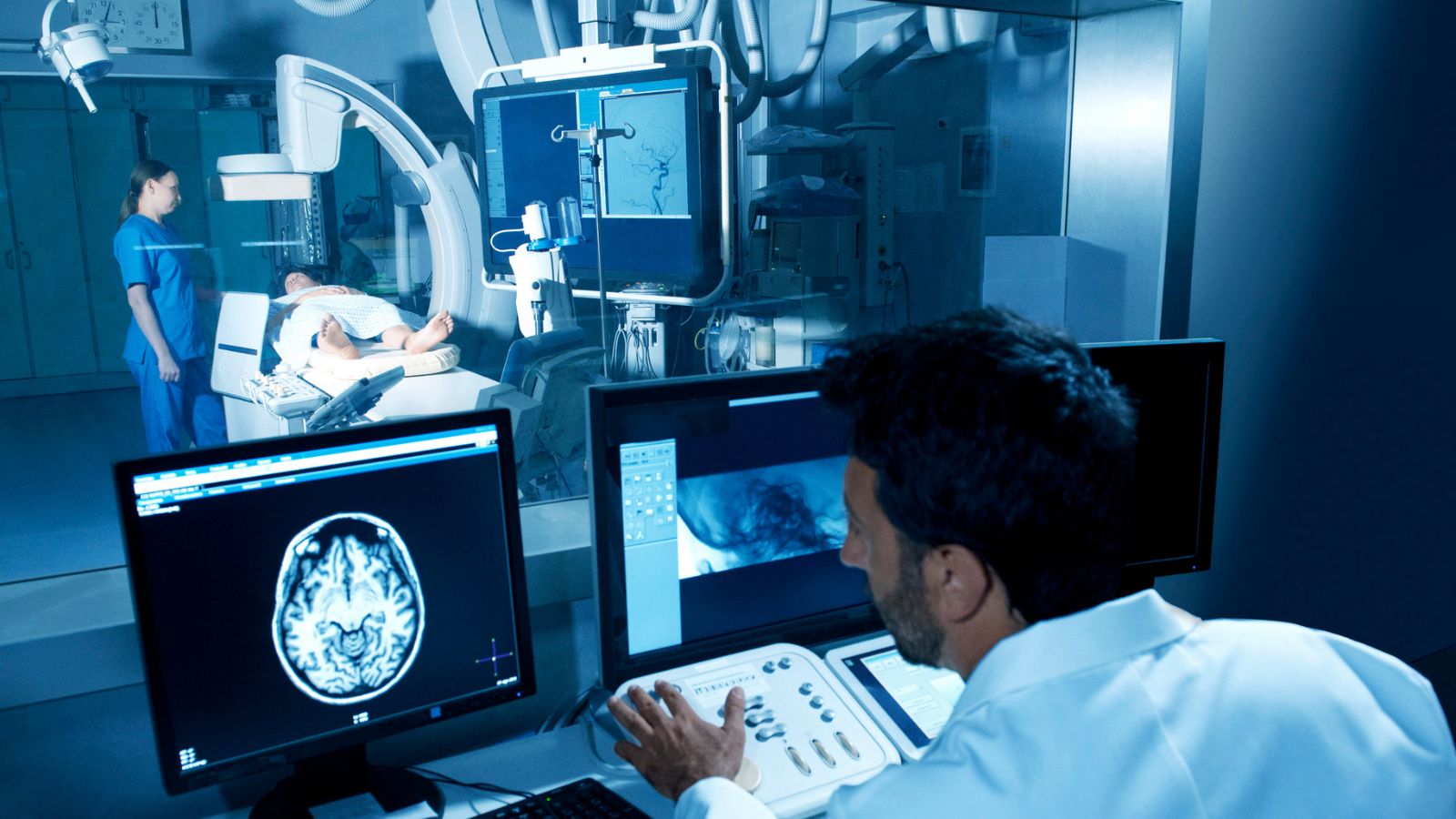
In vitro diagnostic devices are extensively used in hospitals and clinical laboratories to support a wide range of diagnostic procedures. From routine blood tests to advanced genetic screening, IVDs provide critical data that assist physicians in diagnosing conditions, selecting treatments, and monitoring patient progress. Their reliability and speed help streamline workflows and ensure accurate, timely medical decisions.
The rise of consumer health awareness and technological advancement has spurred growth in at-home IVD testing. Devices such as blood glucose meters, pregnancy tests, and COVID-19 antigen kits enable individuals to monitor their health independently. These solutions empower patients, improve compliance with treatment, and reduce the burden on healthcare facilities, especially in remote or underserved areas.
IVDs play a pivotal role not only in diagnosis but also in disease prevention and long-term monitoring. For instance, regular cholesterol or HbA1c testing helps manage chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease and diabetes. In infectious disease control, early detection through IVDs aids in preventing outbreaks. Their use in population screening programs——such as for cancer or genetic disorders——demonstrates their value in proactive healthcare strategies.

Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and immunoassay technologies form the backbone of modern IVD testing. PCR is widely used for detecting infectious agents such as viruses and bacteria by amplifying DNA or RNA sequences with high precision. Immunoassays, including ELISA and lateral flow tests, detect specific proteins or antibodies and are essential in areas like hormone analysis and drug screening. Molecular diagnostics further extend IVD capabilities to identify genetic mutations, hereditary disorders, and cancer biomarkers, enabling highly personalized and preventive care.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming IVD through enhanced data interpretation and predictive analytics. These technologies can analyze complex diagnostic patterns and assist clinicians in identifying subtle abnormalities that may go unnoticed by conventional methods. AI-driven tools also help reduce false positives/negatives and enable automated interpretation of imaging or genomic data, improving diagnostic efficiency and accuracy.
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies with IVD devices is enabling continuous, real-time monitoring of patients. Wearable sensors and connected diagnostic platforms transmit data to healthcare providers instantly, supporting faster response times and better chronic disease management. This connectivity also facilitates remote diagnostics, expanding access to care in rural or isolated locations and enhancing telehealth services.
IVD devices enable early detection of diseases, often before symptoms appear. This early intervention improves patient prognosis by allowing timely treatment and reducing the progression of illnesses. For conditions like cancer, diabetes, and infectious diseases, early diagnosis significantly enhances survival rates and treatment outcomes.
By streamlining diagnostic workflows and minimizing unnecessary treatments, IVDs contribute to more efficient and cost-effective healthcare delivery. Accurate test results guide clinicians toward the most appropriate therapies, avoiding trial-and-error approaches. This not only reduces healthcare costs but also enhances resource utilization across healthcare systems.
Timely and precise diagnostics through IVDs help manage chronic diseases and detect complications early, thereby reducing the need for hospital admissions. Patients benefit from fewer disruptions to daily life, and hospitals benefit from lower occupancy rates and operational stress. In public health, widespread IVD usage can help alleviate the burden on overwhelmed healthcare systems during disease outbreaks.
Despite rapid advancements, many IVD technologies still face limitations related to sensitivity, specificity, and scalability. Some devices may yield false positives or negatives, leading to misdiagnosis or unnecessary treatment. Operationally, integrating new diagnostic tools into existing hospital systems can be complex and resource-intensive, especially in settings with limited infrastructure.
As IVD devices increasingly connect to digital health platforms and cloud-based systems, concerns over data privacy and cybersecurity have grown. Patient health data must be securely stored and transmitted, requiring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Breaches can erode patient trust and lead to significant legal and financial repercussions for manufacturers and healthcare providers alike.
Access to high-quality diagnostic devices remains a challenge in low-income and underserved regions. The cost of IVD equipment, maintenance, and training can be prohibitive, limiting adoption and effectiveness. To bridge this gap, public-private partnerships and affordable innovation models are essential for ensuring that diagnostic advancements benefit global health equity.

Choosing a reliable IVD manufacturer is critical for ensuring product quality, regulatory compliance, and ongoing support. Key factors to consider include:
To assess the suitability of a supplier, ask questions such as:
Autobio Diagnostics is a trusted global leader in the development and manufacturing of high-quality IVD devices. With a strong focus on innovation, regulatory compliance, and customer satisfaction, Autobio provides a wide range of solutions for clinical diagnostics, from immunoassays to molecular tests. Their extensive product portfolio, dedicated R&D team, and global distribution network make them an ideal partner for healthcare institutions seeking reliable and forward-thinking diagnostic technologies.
IVD devices have played a crucial role in the early detection and containment of infectious diseases worldwide. During the COVID-19 pandemic, rapid antigen and PCR tests enabled mass screening, travel monitoring, and timely clinical interventions. Companies like Autobio deployed scalable diagnostic kits that supported frontline healthcare efforts and public health campaigns across numerous countries.
In the realm of genetics, IVDs are revolutionizing diagnostics through advanced testing for inherited disorders, carrier status, and chromosomal anomalies. For example, prenatal screening for conditions like Down syndrome and cystic fibrosis allows expectant parents to make informed decisions. Oncology-focused IVDs help identify gene mutations, enabling clinicians to match patients with targeted therapies more effectively.
Personalized medicine is increasingly reliant on tailored diagnostics that reflect an individual's unique genetic and biological profile. IVD manufacturers now offer custom assays and test panels to support personalized treatment plans, especially in oncology and rare disease management. Autobio, for instance, collaborates with clinical partners to develop customized IVD platforms that enhance treatment precision and patient care outcomes.

The future of in vitro diagnostics is poised for groundbreaking innovations that will enhance speed, accuracy, and accessibility. Technologies such as CRISPR-based diagnostics, microfluidics, and lab-on-a-chip platforms are expected to enable ultra-sensitive and rapid testing. These advancements will further reduce turnaround times and allow diagnostics to be performed in virtually any setting, including rural and low-resource environments.
As the IVD industry evolves, regulatory frameworks are also adapting to accommodate new technologies and testing models. Regulatory bodies are emphasizing faster approvals for high-priority diagnostic tools, especially those addressing public health threats. Meanwhile, the convergence of software and hardware in diagnostic devices is prompting regulators to introduce new categories and guidance for software as a medical device (SaMD).
Patients are becoming more informed and proactive about their health, driving demand for faster, more accessible, and user-friendly diagnostic solutions. The growing popularity of home testing kits and mobile health apps reflects this shift. In response, IVD manufacturers are investing in design improvements, user education, and direct-to-consumer strategies to meet evolving expectations and foster long-term engagement with their products.
IVDs can diagnose a wide range of conditions, including infectious diseases (e.g., COVID-19, HIV, hepatitis), chronic diseases (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular disorders), genetic conditions, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. They are also used in drug testing, fertility assessments, and therapeutic monitoring.
IVD accuracy depends on the type of test, the quality of the device, and adherence to usage guidelines. Most modern IVDs are highly accurate when used correctly and validated through clinical studies. Regulatory bodies like the FDA and CE require rigorous performance standards before market approval.
Yes, many IVD tests are designed for safe and convenient at-home use. Examples include glucose meters, pregnancy tests, and rapid antigen tests. These devices are user-friendly and come with detailed instructions. However, users should always follow the manufacturer's guidelines to ensure accurate results.
The future of IVD technology lies in greater personalization, faster turnaround times, and digital integration. Emerging trends include AI-powered diagnostics, real-time remote monitoring, and wearable testing solutions. These innovations will make diagnostics more accessible and data-driven.
Internationally, IVDs are regulated by agencies such as the U.S. FDA and the European Union's IVDR system. Manufacturers must demonstrate safety, performance, and compliance with ISO standards. Many countries have adopted harmonized guidelines from organizations like the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF).
Yes, many manufacturers offer customized IVD solutions tailored to the unique needs of hospitals, research labs, or specialized clinics. Customization may include assay development, software integration, or workflow optimization, helping institutions achieve better diagnostic performance and efficiency.
In vitro diagnostic medical devices have become fundamental tools in modern healthcare, enabling earlier detection, personalized treatment, and better patient outcomes. As the global IVD market continues to grow, innovations in technology, data integration, and accessibility are transforming how diagnostics are delivered and used. Despite regulatory and operational challenges, the benefits of IVDs far outweigh the barriers, particularly when backed by strong compliance and strategic manufacturing partnerships.
Autobio Diagnostics remains at the forefront of the IVD industry, offering cutting-edge diagnostic solutions that meet global quality and safety standards. Through continuous research and development, global outreach, and a strong customer focus, Autobio supports healthcare providers in delivering accurate and timely diagnostics across diverse clinical environments. Their commitment to innovation and quality positions them as a reliable partner in the evolving landscape of in vitro diagnostics.