

Sex hormones are steroid hormones synthesized in the gonad, placenta, adrenal cortex zona reticularis as well as other tissues. They have the physiological functions of facilitating the maturation of sexual organs and the development of secondary sexual characteristics as well as maintaining sexual functions. Clinically, sex hormones are often detected by serological methods.
*Autobio is committed to improving the quality of products and services. The specifications and parameters of products are subject to the product manual.
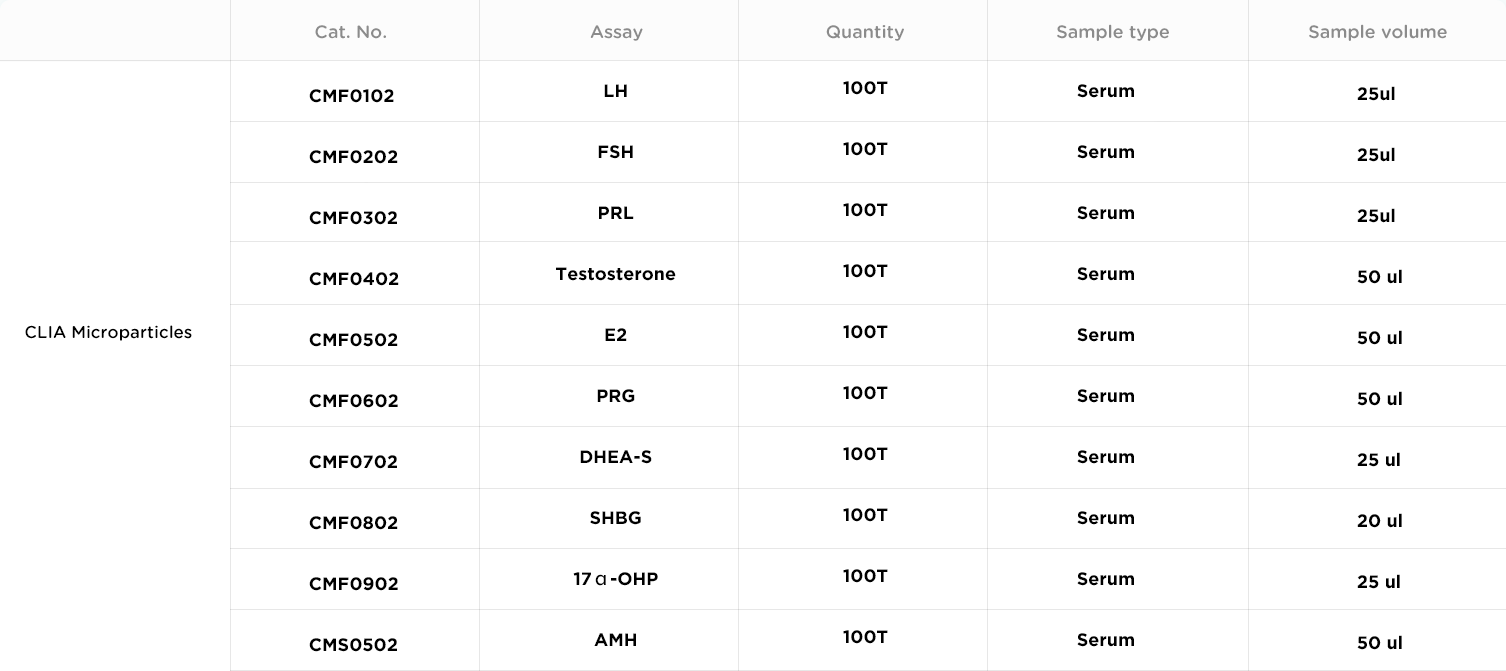
Luteotropic hormone (LH) is a gonadotropin secreted by the pituitary.Its secretion is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone produced by the hypothalamus, and also by female menstrual cycle. LH can facilitate female ovulation and corpus luteum formation, and stimulate the corpus luteum to produce progesterone and oestrogen. In male body, LH can facilitate the synthesis and secretion of testosterone.
Human follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin secreted by anterior pituitary. For females, FSH can facilitate follicle to maturate and secrete oestrogen. For males, FSH is required to regulate vas deferens growth and maintain sperm production. Males with azoospermia and oligospermia usually have an elevated FSH level.
Prolactin (PRL) is secreted by anterior pituitary in both male and female.It plays an important role in the growth and development of the organism and mammary glands, lactation, gonad development and the regulation of water-electrolyte metabolism.In males, it is also important to the growth of gonad and accessory gonad and maintaining their functionality.
Testosterone is produced by leydig cells.In male's blood circulation, 95% of the testosterone is secreted by testicles, whereas in women's blood, nearly all testosterone is produced through androstenedione metabolism. In males, the assessment of testosterone level is mainly used in the auxiliary diagnosis of precocious puberty, puberty retardation, hypogonadism, azoospermia and oligospermia. In females, it is mainly used to evaluate hirsutism, hair loss and menstrual abnormalities.
Estradiol (E2) is a type of steroid hormone. It is secreted by the testicles in males and by the ovary in non-pregnant females. In blood, most E2 are bound to sex hormone-binding globulin.Only 1-2% remains free. Female E2 level can be used to judge the ovarian follicle maturity and evaluate menstrual abnormalities. E2 level elevation in males is associated with diseases like feminization syndrome and gynecomastia.
Progesterone(PRG) works with oestrogen to together regulate the functionality of menstrual cycle-related appendant organs. In non-pregnant females, progesterone is primarily secreted by corpus luteum, whereas in pregnant women it is primarily secreted by the placenta. The adrenal cortex of both males and females and the testicles in males can also secrete a small amount of progesterone. Clincally, Progesterone level can be used to judge the occurrence of ovulation and to evaluate the functionality of corpus luteum in non-pregnant females.
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) is mainly secreted by adrenal cortex, while the ovary in females and the testicles in males can also secrete a small amount. DHEA-S assessment can help distinguish the source of androgen production, diagnose the benign and malignant tumors in adrenal glands and adrenal hyperplasia, as well as distinguish benign and malignant tumors in the ovary that cause similar symptoms. DHEA-S assessment is also an important measure in the auxiliary diagnosis of hirsutism and virilization in females.
Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) is a carrier protein that transports sex hormones. One SHBG molecule can be associated with one sex hormone protein.SHBG level reflects the concentration of free testosterone in the organism.
17α-Hydroxyprogesterone (17ɑ-OHP) is produced by adrenal cortex and gonad.Its progestational activity is very low. Clinically, its assessment is used to diagnose and distinguish congenital adrenal associated with hyperplasia 21-hydroxylase deficiency.It is also used to analyze male and female acne vulgaris in both, male baldness and unexplained infertility.
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) is a hormone secreted by granule cells in the growing follicles of an organism's ovary, which play an important role in regulating follicle activity. Serum AMH assessment can reflect ovarian reserve capacity in an early stage: the higher the AMH level, the higher the ovarian reserve. AMH secretion is not affected by the female menstrual cycle, and therefore its assessment is flexible in time.
[1] Xiangjun Zhang, Dianting Zhang, Hongjie Chen, Jun Wang, Ninggang Yang, Jun Zhang, Xinning Yu, Zhong Liang, Yuanming Han, Analyzing the diagnosis of hyperprolactinemia-induced male sexual dysfunction [J] China Medicine and Pharmacy, 2013,3(09):51-52+69.
[2] Macut D, Milutinović DV, Rašić-Marković A, Nestorov J, Bjekić-Macut J, Stanojlović O. A decade in female reproduction: an endocrine view of the past and into the future. Hormones (Athens). 2018 Dec;17(4):497-505.